How to care for children with extremely low body weight
“See these kids? They were born at 24 and 25 weeks with a body weight of only 500 and 600 grams, ”Oleg Ionov, head of the neonatal intensive care unit, points to two adjacent boxes.
“Imagine - the child had to be in the womb for another half of the term. After birth, he is completely unadapted to life - he cannot breathe on his own, and all body systems are not ready to accept mother's milk, ”Oleg Ionov lifts the cape on the box, showing a tiny body that looks more like a realistic doll than a living child.
Director of the Center Gennady Tikhonovich Sukhikh with colleagues
Oleg Ionov opens transparent boxes with babies especially for us. Most of the time they are covered with thick cloaks so that the visual system matures in the twilight. The situation on the other side of the glass should resemble the mother's womb as much as possible. Inside the box should be dark, warm and quiet.
According to WHO recommendations, the infant's viability limit starts at 500 g. Previously, this figure was twice as much - a fetus less than 1000 g, roughly speaking, was considered a miscarriage. Nevertheless, today children are successfully discharged from the intensive care unit of newborns, who at birth did not even reach the cherished 500 grams.
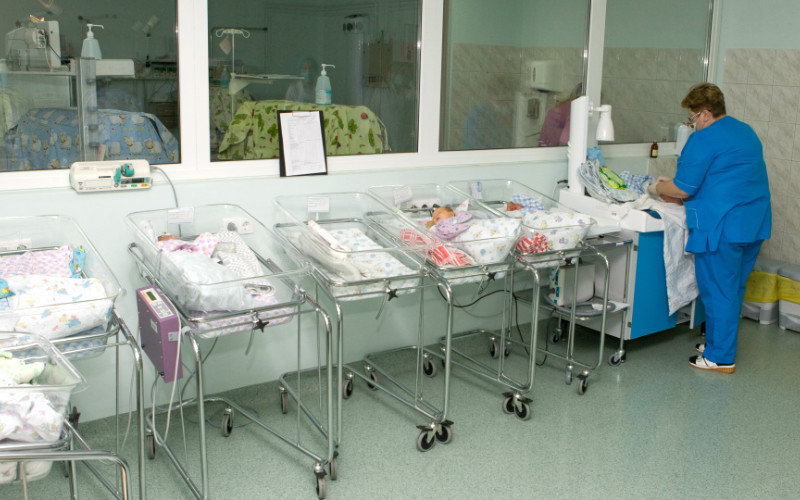
The neonatal intensive care unit is more like the location of a science fiction movie. Here, no one fusses and runs around with medicines. Almost all the work is done by machines. Nurses come into the room to record physiological data and make sure everything is going according to plan. The plan itself is developed by a team of doctors - individual for each patient. And depending on the physiological changes, it is constantly adjusted.
“Our center has good results not just because we use good medicines or good equipment, but because we have developed the right system - when to use this or that method, when to switch from one to another, when to use this medicine, and nothing else,” lists the components of successful work Oleg Ionov.

Hard breathing
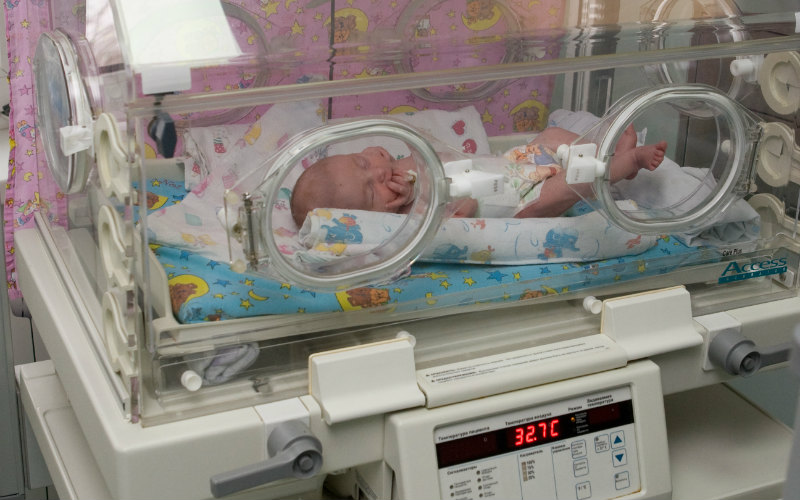
As soon as the baby is born, a whole nursing technology is launched. Taking into account the age and comorbidities for a tiny patient, possible risks and a number of appropriate drugs are calculated, because without the help of doctors, premature babies cannot even take their first breath.
“We immediately give him a pulmonary surfactant – this is a natural drug that partially turns immature lungs into mature ones. This is a complex mechanism that allows you to open the lungs of a child, because they bear little resemblance to the lungs of an adult,” says Oleg Ionov.
From the delivery room to the resuscitation room, the child is brought on respiratory support and then, depending on the severity, he is switched either to a ventilator (when the breathing tube is directly in the trachea) or transferred to non-invasive respiratory support.
“It looks like this,” Oleg Ionov points to one of the boxes. - You see, the baby breathes on his own, but he has cannulas in his nose, they also inhale and exhale, but at the same time, the child controls most of the work of breathing. Moreover, now the devices are smart, with the help of special sensors they feel how the child wants to breathe, and adjust to it.”

Instead of mom
Just imagine: the child received in the womb all the necessary amino acids, fats, carbohydrates, microelements - and suddenly this connection was broken. The task of doctors is to calculate what substances and in what volume the baby should receive now, and how this data should change as it grows (or, conversely, its absence). This painstaking analysis is the art of neonatologists.
“In the department, under sterile conditions, we create special combined nutrient mixtures, which are then connected to the child. Then we examine his blood, see if the child absorbs everything well. After that, we make a correction, and if everything goes well, we try to feed the child through the mouth,” explains Oleg Ionov. – Gradually, we adapt the baby to formulas for premature babies or to breast milk, that is, we increase the dose of what is given through the mouth and reduce the dosage of what is given through the veins. We evaluate how the baby grows and compare it with certain tables.” “We can correct the calorie content and even the protein concentration in milk. There are special technologies and drugs that enrich breast milk, because breast milk during prematurity has a very low protein content,” says Oleg Ionov, pointing to a structure hanging on the wall. - For example, now the feeding is over. You see special syringe pumps, they are inclined, because in breast milk, this is also a whole technology, fat floats up. And in order for the child to receive everything, including fats, so that they do not remain in the adapter, you need to know at what angle to put this syringe.
The task of doctors is to constantly monitor the condition of small patients, check with growth tables, adjust the ratio of nutrients in mixtures, monitor the development of all organs and systems, track pain impulses and many other aspects that make up the work of a neonatologist. The work is titanic, but the results are more than worth the effort, especially when another patient is discharged from the department.
