Chickenpox - causes, symptoms and diagnosis, drug treatment of chickenpox in children and adults, diet food, photo. How many days after infection do the first signs of the disease appear? Does the chickenpox vaccine help?
Or chickenpox - an infectious viral disease, accompanied by intoxication and spotty-bubble rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. Chickenpox is very contagious - almost everyone who has contact with the patient gets sick and has not been sick before. After the disease, a stable lifelong immunity is developed.
It is noteworthy that the severity of the course of the disease depends on age. Children carry the disease in a mild form, and adolescents and adults in a more severe form. They also have a high risk of complications. Pediatricians point out that in children with an active temperament, the rash is more abundant than in calm and phlegmatic ones.
Until the 17th century, chickenpox was considered a deadly disease - a type of smallpox. Since then, the name "chicken pox" has remained. As a separate disease, chickenpox began to be isolated in 1772, and the virus was only investigated in the middle of the 20th century.
Causes of chickenpox
The causative agent of chickenpox is the human herpes virus type 3. The exciter has rather large dimensions - from 150 to 200 nm. Its genetic information is contained in a DNA molecule surrounded by a lipid membrane.The virus multiplies only in the human body, and in the environment it quickly dies when it dries out, under the influence of UV rays and any means for disinfection. In droplets of mucus and saliva lasts up to 15 minutes. Highly volatile - spreads with air flow.
Epidemiology of chickenpox
Source infections - a person with chickenpox, rarely shingles. It becomes contagious during the last 2 days of the incubation period and 7-9 days after the onset of the rash.Transmission route- airborne. From the patient's body, the virus is excreted with droplets of saliva when talking, coughing and breathing. With a current of air, it is brought into other rooms. Due to the fact that the virus is unstable in the external environment, it is not transmitted through objects or through third parties. A vertical route of infection is also possible, when the virus passes from an infected mother to the fetus through the placenta.
Susceptibility to the virus chicken pox is very high - almost 100% of people who have not been ill before fall ill. This means that if a person who does not have immunity communicated with a sick person, then he is guaranteed to get sick.
chickenpox incubation period(from infection to the appearance of the first symptoms) lasts 10-21 days, on average 14-17 days.
After an illness, the body develops a stable lifelong immunity. It is believed that it is possible to get chickenpox again only in exceptional cases. Infants for the first 2-3 months of life are protected by innate immunity. Antibodies to the chickenpox virus are transmitted to them from the mother transplacentally. In the future, the titer of antibodies in the blood decreases, and the child may get sick.
The number of patients with chickenpox increases in the autumn-winter period. Large outbreaks occur in kindergartens, schools and boarding schools, while almost all children are infected who have not been sick before. Thanks to this feature, by the age of 15-16, 70% of the population already have immunity to chickenpox, acquired after an illness. People who do not get sick in childhood are at risk of becoming infected later in life.
Chickenpox: what is the route of transmission of the varicella zoster virus, how you can get infected, how many days the incubation period lasts and the disease itself - video
Pathogenesis
incubation period. The virus enters the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. It penetrates the cells and rebuilds them, forcing them to produce new viral particles. In the future, the virus spreads throughout the body with a current of lymph. At the end of the incubation period, it is released into the blood.Disease development. The first symptoms of chickenpox are associated with viremia - the presence of a virus in the blood. In patients, the temperature rises and intoxication develops due to poisoning of the body with the waste products of the virus.
Further, the chickenpox virus selectively affects the cells of the skin and mucous membranes, which is manifested by characteristic rashes - a maculopapular rash. The virus also penetrates into the nerve ganglia responsible for the innervation of the skin. In addition, it depresses the immune system by disrupting the function of T-lymphocytes. In this regard, the patient may exacerbate chronic diseases. Children during and after chickenpox become especially susceptible to viral and bacterial infections. 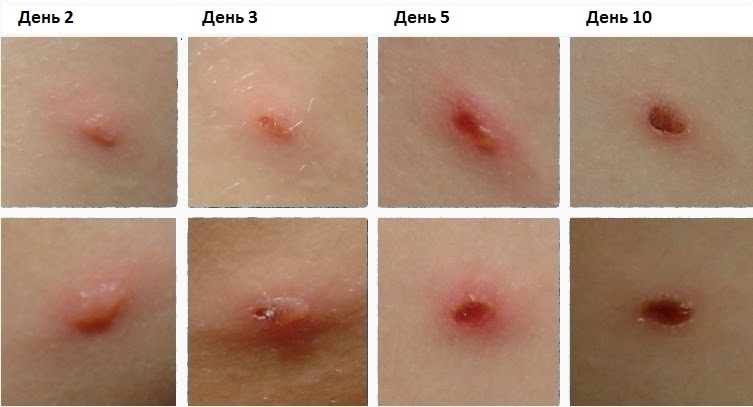
Recovery and the formation of immunity. The immune system recognizes the virus and produces specific antibodies to fight it. These immunoglobulins are the basis of stable immunity. When re-infected, they quickly recognize and destroy the virus.
When treating chickenpox in children and mild forms in adults, it is enough to bring down the temperature and process the elements of the rash. The need for medication is determined by the doctor.
Chickenpox care
 Caring for a child with chickenpox occupies a central place in the treatment of the disease. Proper treatment of the skin and mucous membranes helps to prevent the attachment of a bacterial infection and the development of complications.
Caring for a child with chickenpox occupies a central place in the treatment of the disease. Proper treatment of the skin and mucous membranes helps to prevent the attachment of a bacterial infection and the development of complications. - Bed rest during fever. Children with mild illness and a normal temperature do not need to limit activity.
- To remove toxins, it is recommended to drink more fluids.
- Elements of a rash on the skin are treated:
- 10% solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate);
- 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green.
- To reduce itching, it is recommended to lubricate the skin:
- camphor oil;
- vodka.
- Children should keep their nails short to prevent scratching and infection.
- Rinse your mouth after eating:
- furatsilina solution - 2 tablets per glass of water;
- weak pink solution of potassium permanganate.
- Treat aphthae in the oral cavity and on the genitals:
- methylene blue;
- an aqueous solution of brilliant green;
- For rashes on the genitals:
- sitz baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- frequent washing with a solution of furacilin;
- to accelerate the healing of aft, a gauze strip is impregnated with sea buckthorn oil and applied to the affected area.
- In case of damage to the conjunctiva of the eye:
- washed with black tea or chamomile infusion;
- instilled with a 30% solution of albucid (sulfacyl sodium) or 1% solution of protargol.
- To reduce itching:
- baths with oatmeal or cornstarch. Dissolve 1 cup of flour in 3 cups of warm water and add the mixture to a bath of warm water.
- In the hot season, it is recommended to take a warm shower as needed. Water cleanses the skin of sweat and bacteria, reducing itching.
- After water procedures, the skin is blotted with a soft cloth that absorbs moisture well.
- Daily change of underwear and bed linen is required. Clothing should be loose and made from natural fabrics so as not to injure the papules. It is important that the patient does not overheat, as sweating increases itching.
- Bread made from premium flour.
- Soups, not greasy, not rich.
- Animal and poultry meat in the form of souffle, meatballs, steam cutlets and meatballs.
- Milk and dairy products - yogurt, kefir, low-fat cottage cheese.
- Soft-boiled eggs, steam omelet.
- Semi-liquid cereals with the addition of milk or broth.
- Steamed vegetables - vegetable stew, caviar, mashed potatoes.
- Berries and non-hard fruits, peeled. Juices, compotes, kissels, mousses, jelly from them.
- Rosehip decoction, weak tea with honey or milk.
- Fatty and fried foods.
- Spicy snacks.
- Smoked products - meat, fish, sausage.
- Products that cause gas formation - cabbage, radish, radish, legumes.
- Sharp cheeses, fat sour cream, cream.
- Strong tea, coffee, spirits.
- Purulent skin lesions. The most common complications are abscesses, boils, phlegmon. They are formed with suppuration of the skin and subcutaneous tissue around the infected papule. The cause of development may be hidden foci of infection, when streptococci and staphylococci are carried throughout the body with blood flow. Also, one combed bubble can become the entrance gate for an infection that spreads to other areas of the skin.
- Scars, pockmarks - cicatricial changes appear at the site of deep skin lesions, combed and festering vesicles.
- Chickenpox pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs associated with the penetration of the virus into the alveoli. Against the background of a massive rash and a rise in temperature, the patient develops shortness of breath, cough, chest pain, blood-streaked sputum, cyanosis - blue skin on the peripheral parts of the body (earlobes, nose, fingers).
- Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain caused by the destruction of nerve cells under the influence of the chickenpox virus. Appears during the extinction of the disease on the 5-20th day after the onset of the rash. It is characterized by a rise in temperature, headache, lethargy, impaired consciousness, nausea, vomiting. After a few days, the main symptoms of mental disorders, convulsions, paresis of the limbs appear. Varicella encephalitis is characterized by reversibility of changes.
- Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle caused by the varicella-zoster virus. In patients, the temperature rises, there is severe weakness, heart rhythm disturbance, tachycardia, chest pain.
- Lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodescaused by the spread of infection through the lymphatic system. The axillary, inguinal and cervical lymph nodes are predominantly affected. They are enlarged, when probing, there is a slight soreness, the skin over them is reddened.
- Nephritis is an inflammation of the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys. Develops by the end of the second week of the disease. In patients, the temperature rises sharply, there is a headache, pain in the abdomen and lower back, swelling, and the volume of urine excreted decreases.
- Fetal damage in pregnant women. Chickenpox in the early stages can lead to fetal underdevelopment, rarely to miscarriage. Chickenpox in the last weeks before childbirth can cause congenital chickenpox syndrome.
- Progressive deterioration of the general condition after a temporary improvement.
- Prolonged fever, severe weakness, drowsiness, refusal to drink - indicate severe intoxication.
- Long period of rashes more than 5 days.
- Purulent contents inside the vesicles, an inflammatory rim around the vesicles, a painful rash - the addition of a purulent skin infection.
- Severe cough, hemoptysis, shortness of breath - possible viral damage to the lungs.
- Shortness of breath and chest pain, cyanosis (cyanosis of the skin) indicate heart damage.
- Headaches, numbness of the neck and limbs, back pain, convulsions, frequent vomiting are signs of damage to the nervous system.
- Violation of consciousness, impaired speech - indicate inflammation of the brain.
- Pain in the eyes, a rash on the conjunctiva occurs when the eyes are damaged.
- Severe abdominal pain - may indicate a generalized form with damage to internal organs.
- During the 21st day, contacts of all ages need to be given special attention. With an increase in temperature, redness of the mucous membrane of the throat, or any rashes on the skin, it is necessary to call a doctor.
- Contact children under 7 years of age (attending kindergartens) are not allowed in preschool institutions from the 11th to the 21st day from the moment of contact. If there is no exact date of contact, then the contact child is isolated for 21 days.
- Contact children over 7 years old and adults. Not subject to separation, they can continue to go to school and visit public places until the first signs of illness appear.
- Emergency contact vaccination may be recommended for immunocompromised children and pregnant women. Okavax or anti-varicella immunoglobulin are used. The introduction of these drugs in the first three days after contact protects against the development of the disease.
- A significant decrease in immunity - HIV infection, long-term use of systemic corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, strict diets and starvation, physical and mental exhaustion.
- Low level of anti-varicella antibodies. This situation is possible if a person has had chickenpox at an early age. In the first year of life, the immune system is not sufficiently developed, so it may not provide adequate protection.
- Infection with another type of herpes virus. Rash can cause 1, 2 and 6 types.
- Diagnostic error. A blistering rash can be a symptom of more than just chickenpox. Perhaps for the first time, vesicular rickettsiosis, flea bites or other insect bites were mistaken for chickenpox.
- During the first 8-10 weeks of pregnancy, chickenpox can cause miscarriage or miscarriage. If this does not happen, then the risk of complications in the fetus is less than 5%.
- 2-3rd trimester, the risk to the fetus is minimal - does not exceed 2%.
- A period of more than 37 weeks - the risk of developing congenital chickenpox in a child reaches 25%.
Folk methods of treatment
Mild forms of chickenpox can be treated with folk remedies. Medicinal plants stimulate the production of antiviral antibodies, strengthen the immune system and help cleanse the skin from rashes.
Nutrition for chickenpox (diet)
 A diet for chickenpox should be aimed at removing toxins from the body and stimulating the immune system. Boiled or steamed food helps to facilitate digestion. It is desirable that the dishes are mashed and not hot. This is especially important for patients with rashes on the oral mucosa.
A diet for chickenpox should be aimed at removing toxins from the body and stimulating the immune system. Boiled or steamed food helps to facilitate digestion. It is desirable that the dishes are mashed and not hot. This is especially important for patients with rashes on the oral mucosa. When the first symptoms of chickenpox appear, the appetite deteriorates significantly. Do not force the patient to eat, especially during the period of fever. Offer food during those hours when you managed to bring down the temperature. It is advisable to eat little, but often - 4-5 times a day.
basis food should become:
Chickenpox treatment: antipyretic, antiviral, antihistamines, rash treatment, hygiene measures, nutrition - video
Effects
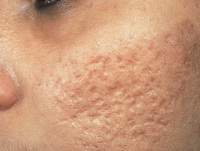 Chickenpox is considered a benign disease and is relatively easy to tolerate, especially in childhood. However, 5% of patients develop complications, more often these are adults with a weakened immune system.
Chickenpox is considered a benign disease and is relatively easy to tolerate, especially in childhood. However, 5% of patients develop complications, more often these are adults with a weakened immune system. Chickenpox: complications in infants; how chickenpox proceeds during pregnancy, how to avoid negative consequences for the fetus; how to eliminate scars and scars after chickenpox; when you can wash (pediatrician's recommendations) - video
Chickenpox prevention
Preventive measures for patients with chickenpoxPrevention of chickenpox is based on the timely detection and isolation of the patient: 
Preventive measures regarding contact persons
Contacts are considered to be people who communicated with the patient or were in the same room with him 2 days before the onset of the rash and up to the 8th day from the moment the last element of the rash appeared:
What is the prognosis for chickenpox?
The prognosis for chickenpox is usually good. Complications occur in debilitated patients, people suffering from immunodeficiency and severe systemic diseases.Answers to frequently asked questions
Is it possible to get chickenpox a second time?
Re-infection with chickenpox is possible provided that the level of IgG antibodies to the varicella-zoster virus is not high enough in the person's blood. A few decades ago, recurrent chickenpox was an exception, and now it is believed that the probability is up to 10%.Causes of re-infection with chickenpox:
When is a person with chickenpox contagious?
A patient with chickenpox is considered contagious 2 days before the rash appears and 5 days after the last element appears.In mild and moderate forms, a patient with chickenpox is contagious for 9 days from the moment the first pimple appears.
How can you get chickenpox?
100% probability of infection - stay with the patient indoors, public transport. And also in any situations when the patient's saliva gets on the oral mucosa of a healthy person - with a kiss, drinking from one cup, etc. Everyone who has not had chickenpox before becomes infected.The risk is high up to 80% when communicating with a patient on the street - when talking and coughing, drops of saliva spread to a distance of 1-2 meters. If they enter the respiratory mucosa of susceptible people, then infection will occur. However, sunlight and air currents reduce the possibility of infection.
There is no risk of infection through personal belongings and toys of the patient or through third parties. For example, parents of a sick child or a caregiver in whose group there is an outbreak of chickenpox cannot carry the infection.
Is it possible to walk on the street with chickenpox?
Children with mild forms of chickenpox with a normal temperature can walk outside. At the same time, care must be taken to exclude contact with other people. The patient can infect non-ill residents of the entrance and those who are nearby on the street, and for people with a weakened immune system, chickenpox can be very dangerous.Remember that active games, sun exposure and hypothermia are undesirable for a sick child.
Adults should remain in bed until complete recovery. Unwanted physical activity can cause complications.
Is it possible to swim with chickenpox?
Doctors of the "old school" do not recommend wetting the rash, arguing this by the risk of suppuration of the vesicles. Western medicine, on the contrary, advises taking baths to reduce itching. Modern infectious disease specialists recommend taking a shower with severe itching (every 4 hours) or 1 time per day as a normal hygiene procedure.There is a risk of introducing bacteria through the towel. Therefore, it must be clean and ironed with a hot iron. It is acceptable to use soft disposable paper towels.
Is chickenpox dangerous for pregnant women?
 The danger of chickenpox pregnancy depends on the period at which the woman stays.
The danger of chickenpox pregnancy depends on the period at which the woman stays. Treatment of chickenpox in pregnant women. In mild forms, specific therapy is not prescribed, it is enough to drink more liquid and treat the elements of the rash. Recent studies have shown that pregnant women have a low risk of developing pneumonia and other lesions of the internal organs.
In severe forms, treatment is carried out with Acyclovir, which does not adversely affect the fetus. The daily dose is 4 g, the duration of treatment is 7-12 days.
What should a pregnant woman who has had chickenpox do?
Before use, you should consult with a specialist.